Bidirectional Scattering Distribution Function (BSDF)
Defines the way that light transmits and reflects off of an object or material. When light is transmitted or reflected it can have specular components and diffuse components. A BSDF file is used by daylight and energy modeling software to characterize how light interacts with a material such as glass or shade fabric. This detailed property file allows more accurate estimation for energy performance, daylight availability, and rendering accuracy in these tools. 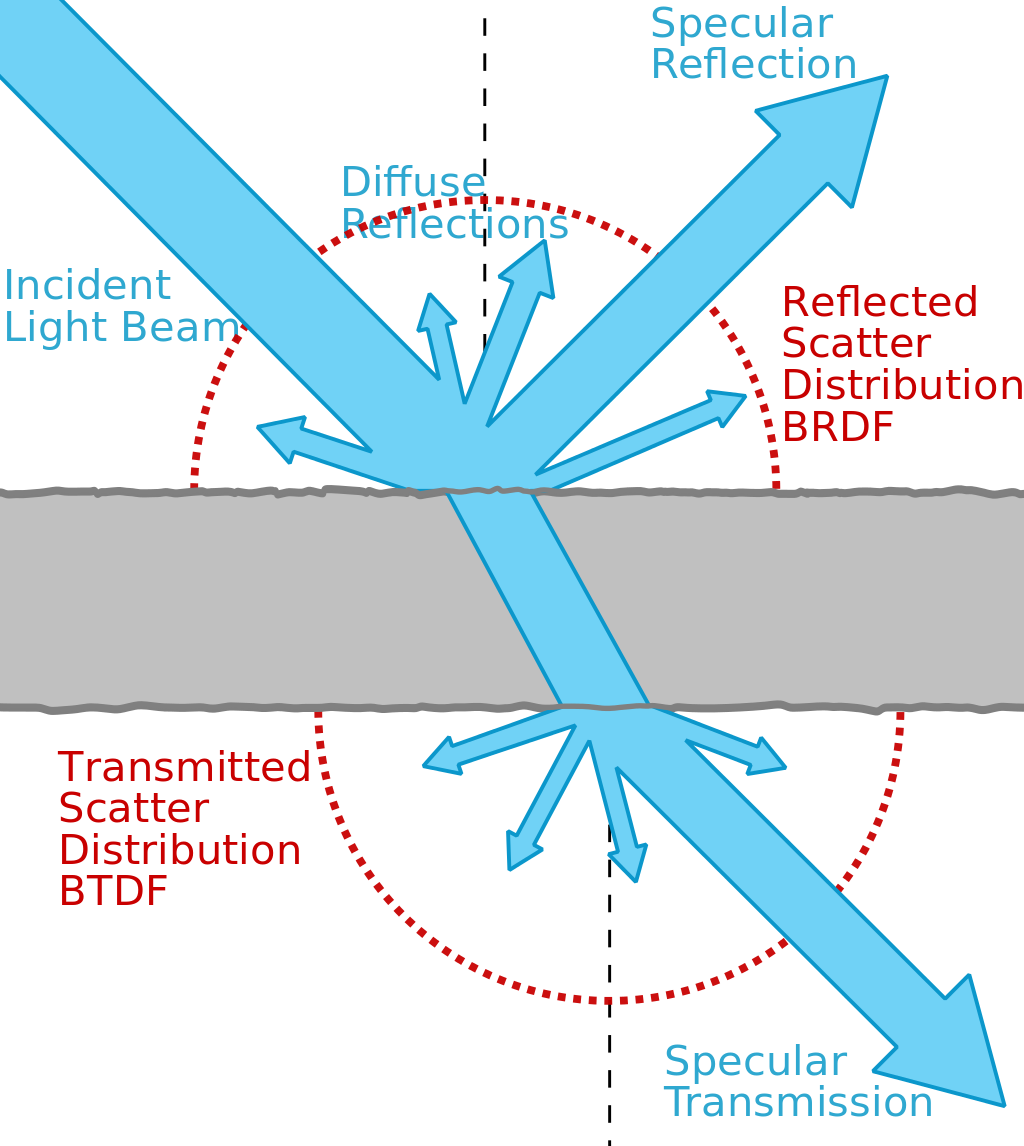
Daylight Autonomy (DA)
The percentage of business hours where the required illuminance can be delivered by daylight alone. In other words, it helps understand for a particular point on the office floor, what percentage of work hours can the lighting needs be met from daylight alone.
Daylight Glare Probability (DGP)
DGP is the probability of a person or group of persons perceiving some level of glare at a given location and view angle
- 0.50 – Critical
- 0.45 – High
- 0.40 – Medium
- 0.35 – Low
A DGP of 33% indicates that there is a 1/3rd likelihood of the occupant (or 33% of the occupants) noticing some level glare. Although this may seem high, with a DGP of 33% the level of glare perceived by the occupants is typically considered “nearly unnoticeable” meaning that it would not affect day to day activities. Conversely, when the DGP exceeds 50%, the level of glare perceived by the occupants is typically considered “very uncomfortable” meaning that it would likely cause serious disruption in day to day activities.
Direct Glare
The perception of uncomfortable brightness caused by high contrast from a light source, such as the sun. When daylighting, direct glare is most commonly experienced when there is direct view of the sun orb and the fabric's openness factor is too high for the application.
Diffuse Glare
The perception of uncomfortable brightness caused by too much light in the field of view. When daylighting, diffuse glare is most commonly experienced when the sky is bright and the shades are open, or when a shade fabric has too high of a visible light transmittance (Tv) for the application.
Dual-sided
Some fabrics have two different properties (most noticeably color) that meet two different needs - one for the side facing the exterior and one facing the interior. Generally, this is done to include a higher solar reflectance on the outside to reflect solar heat gain and improve thermal comfort.
Maximum Usable Width
Each roll of fabric has a maximum width based on the size of the loom on which the fabric is constructed. In some cases,
railroading a fabric can provide a solution for wide shades.
Noise Reduction Coefficient (NRC)
Noise Reduction Coefficient (NRC) is the standard rating for how well a material absorbs sound. NRC is determined by averaging the sound absorption of a material at four different frequencies (250 Hz, 500 Hz, 1000 Hz, 2000Hz). The NRC value is always between 1 and 0. A NRC value of 1 indicates perfect absorption, while a NRC value of 0 indicates all sound is either reflected or transmitted. Generally, a NRC value of 0.5 is considered to offer significant sound absorbing properties.
Openness Factor
Openness factor describes the percentage of light that transmits directly through the fabric. It can be approximated by the percentage of open space in the weave. Simply stated, it varies based on how tightly fabrics are woven - the tighter the weave, the less daylight filters through.
The published values for openness factors are typically nominal or approximate values used to give a general indication of the weave tightness. Although useful, these are not sufficient for evaluating the shading system performance (glare, daylight, and views). Look for the mean openness factor values for accurate performance evaluation.
There are typically three types of fabrics classified by openness factor – Sheer, Translucent/Dim-out, or Blackout fabrics.
- Sheer fabrics have a high transparency, and the openness factor is 1% or higher. Common nominal openness factors for sheer shades are 1%, 3%, 5%, and 10%. These fabrics allow daylight to enter a space and provide a view to the outdoors.
- Translucent or Dim-out fabrics, also referred to as privacy fabrics, have an openness factor between 0% and 1%. These fabrics let in a limited amount of daylight. A view outside will have very little detail - you will only see shapes and shadows.
- Blackout fabrics, or opaque fabrics, have a 0% openness factor and block 100% of daylight. Commercially, blackout fabrics are often used in conference room applications to allow for presentations or video conferences. For total blackout, a side channel is required.
PVC-free
PVC free fabrics have virtually no harmful chemical content (known as VOCs), allowing them to be recycled and are considered more environmentally friendly than other fabric types
Railroadable
Railroading fabric is an option for applications requiring shades wider than the maximum usable width. Railroading rotates the fabric 90 degrees from its typical orientation. If the fabric has a distinct pattern, please note that this pattern will also be rotated 90 degrees, thereby altering the final appearance of the shade. Railroading is best done with a symmetrical weave fabric.
Recyclable
Some solar screen fabrics can be recycled and collected at the end of their life and remanufactured into new products. This allows natural resources, energy and landfill space to be saved.
Recycled Content
Some fabrics have been woven with pre or post- consumer content that was recycled from a previous material or manufacturing process. These fabrics are made totally or partially from scrap material or from material contained in recycled products, like water bottles.
Seamable
Some fabrics can be seamed/welded together in order to increase the size of a railroaded shade beyond its fabric roll width. This technique is used to achieve long, wide shades. If a fabric has a distinct pattern, aligning the pattern during seaming may alter the final appearance of the shade.
Solar Absorption (As)
The percentage of
total incident radiation absorbed by the fabric. A lower figure indicates a low absorption of solar energy. Generally, the published solar absorption is based on the back side (outside) of the fabric to evaluate solar heat absorption.
Solar Reflectance (Rs)
The percentage of
total incident radiation reflected by the fabric. A higher figure is good for controlling heat gain. Generally, the published solar reflectance is based on the back side (outside) of the fabric to evaluate solar heat reflection.
Solar Transmittance (Ts)
The percentage of
total incident radiation transmitted through the fabric. A higher figure indicates more solar energy entering the room.. Generally, the published solar transmittance is based on light transmitting from the back side (outside) to the front side (inside).
Spatial Daylight Autonomy (sDA)
Spatial
daylight autonomy is the area of the space that receives 30 fc (300 lux, the typical ambient light level for offices) for at least 50% of the work hours.
This however does not account for partial daylight received in the space, i.e. anything less than 30 fc (300 lux) but greater than 0 fc (0 lux).
THEIA™ Performance Specification (THEIA Compliant)
The
THEIA™ Performance Specification is a manufacturing specification for solar screen fabrics. By requiring tight manufacturing tolerances around fabric performance criteria, specifically openness factor and visible light transmittance, and defining the testing process and documentation, designers can be confident that the fabric delivered to the project will meet their design intent.
Total Incident Radiation
Total Incident Radiation is measured as a combination of three other values –
Solar Transmittance,
Solar Reflectance and
Solar Absorption. These three values always add up to 100%, or Total Incident Radiation. (Ts = Total Incident Radiation) + Rs + As
Useful Daylight Illuminance (UDI)
UDI is the percentage of business hours where the daylight illuminance is between 20FC (200 lux) and 200FC (2000 lux). This is generally considered a useful light level range, enough light for daylight harvesting but not so much as to be wasteful. For each point in the space, what percentage of work hours do I get enough daylight for daylight harvesting but not so much that it may cause glare for some occupants.
Useful Daylight Zone
The area of a space that receives 30FC (300 lux, the typical ambient light level for offices) from daylight alone for at least 50% of annual work hours. Essentially, this defines the area that gets enough daylight to make use of switched daylight harvesting. However, the area where dimmed daylight harvesting is typically much larger (1.5 times or more).
View Clarity (VCI)
View clarity Index (VCI) estimates the perceived ability to see the exterior environment through a shade fabric. A value of 100% indicates that the fabric provides not obstruction to the view, while a value of 0% indicates that a typical occupant cannot see through the fabric at all. This metric does not take into account the effect of glass properties on view perception.
Visual Transmittance (Tv or VLT)
The Tv value is the percentage of visible light transmission through the fabric. For instance a Tv of 50% indicates that the fabric allows 50% of the light that falls on it to pass through. This is an important measurement for understanding how a shade will help to minimize glare and visual comfort. Typically, a high Tv value can indicate high glare.
Volatile Organic Compound (VOC)
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic chemicals that have a high vapor pressure at ordinary room-temperature conditions. Most scents or odors indicate the presence of VOCs. VOCs that are considered harmful aren't typically acutely toxic, but research shows they can have longer-term health effects. GREENGUARD certification means a product has passed testing for indoor pollutant emissions and can be considered low-VOC.
